计算机网络Chapter4 Network layer 网络层
# Network layer 网络层
# 路由选择routing(确定哪一条路径)
The routing table is constructed according to the specific routing protocol, and the routing table is constantly updated and maintained by exchanging routing information with neighboring routers.
路由表是根据特定的路由协议构建的,通过与相邻路由器交换路由信息,不断更新和维护路由表。
According to the complex distributed algorithm, Dynamically change the route selected.
根据复杂的分布式算法,动态改变所选择的路由。
# 分组转发forwarding(当一个分组到达时采取的动作)
To deal with the data flow through the router, the key operations are forwarding table query, forwarding and related queue management and task scheduling.
The router forwards the user's IP datagrams from the appropriate port based on the forwarding table.
处理通过路由器的数据流,关键操作是转发表查询、转发以及相关的队列管理和任务调度。
路由器根据转发表将用户的IP数据报从合适的端口转发出去。
# Routing Algorithm 路由算法
# Static and Dynamic
# 静态算法:
routes change slowly over time
# 动态算法:
routes change more quickly,Improves performance and flow control性能增强并有利于流量控制
# Routing protocols 路由协议
目的:determine “good” paths (equivalently, routes), from sending hosts to receiving host, through network of routers.
# ⭐️link state 链路状态路由算法 Dijkstra's Algorithm SPF
c(x,y): 节点x到节点y的链路开销; 如果不是直接邻居=∞
D(v): 从源到目标的路径开销的当前值
N': 已知最小代价路径的节点集

# ⭐️Bellman-Ford equation(dynamic programming) (贝尔曼-福德)距离向量方程(动态规划) RIP
重要
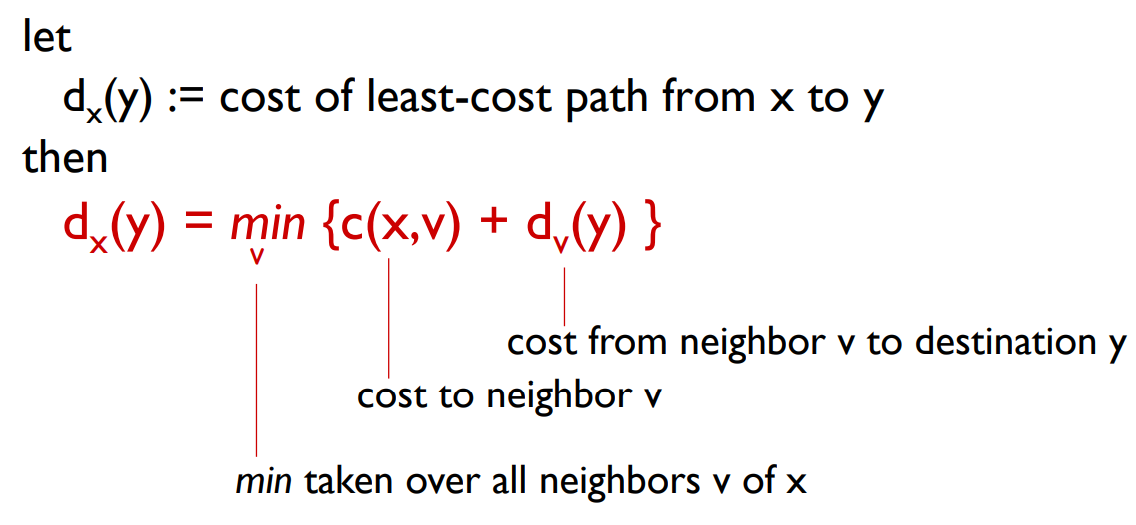
# ⭐️distance vector 距离-向量路由算法 RIP
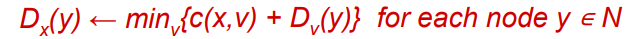 重要!
重要!
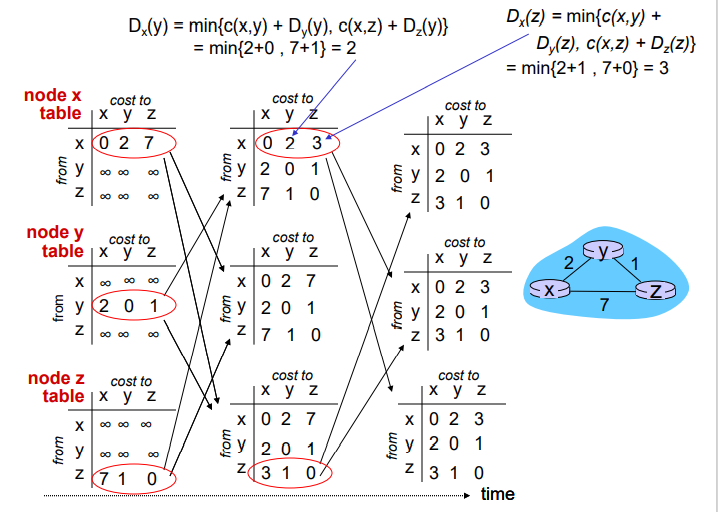
第二布,将无限符号替换为来自其他表的数据,并对自己本身行区域最小值优化,最后的表格则为综合了第二部三个表的最优解的答案(内容完全相同)
# ⭐️link cost changes 链路消耗变化会发生什么?
DV(distance vector)
t0,t1,t2...
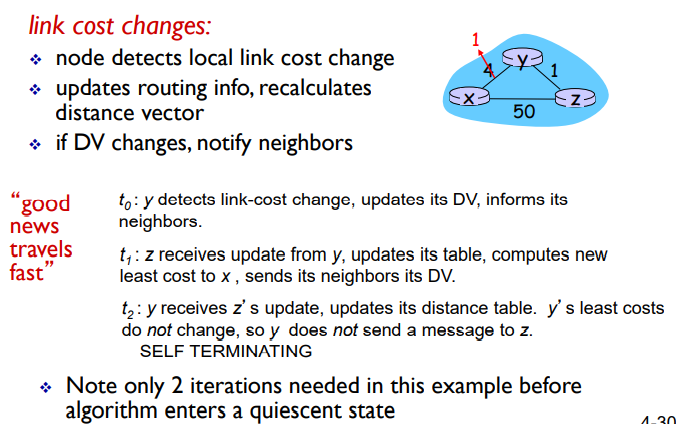
在变成静态之前算法迭代两次
t0: y检测到链路开销的变化,更新DV,通知邻居。
t1: z收到y的更新,更新它的表,计算x的新最小成本,给它的邻居发送DV。
t2: y收到z的更新,更新它的距离表。Y的最小代价不变,所以Y不会向z发送消息。自动终止
