计算机网络Chapter2 Application Layer 应用层
# Application Layer 应用层
# Network Applications
# TCP/IP
These protocols describe the data transmission between the source and destination over the internet
这些协议描述了在internet上源和目的地之间的数据传输
Among these layers, application layer is the 1st layer.
是四层协议,认为物理层和数据链路层统一为 网络接入层 Network access layer
Two different architectures are used in modern network applications:
- client-server architecture (C/S)
- peer-to-peer (P2P) architecture(去中心化的,每个主机都是服务器和客户端)
# FTP File Transfer Protocol
- FTP is a standard network protocol provided by TCP/IP and it is used for exchanging the files from one host to another. 用于在主机之间交换文件
- It is also used for downloading the files to computer from other servers.
- FTP is built on client-server architecture
Types of File Transfer Protocol(FTP):
Control Connection 逐行传输,随时关闭
Data Connection 进程连结,指令开启,传输完关闭
# Socket
A process sends messages into, and receives messages from, the network through a software interface called a socket.
进程通过一个称为套接字的软件接口向网络发送消息,并从网络接收消息。
socket is the door between the client/server process and the TCP connection.
socket是客户端/服务器进程和TCP连接之间的门户
# IP
- IP address
- port number
IP address have two parts i. Network id and ii. Host id If IP address is 192.168.1.32, Network id is 192.168.1 and the host ID will be 32
**Mainly 4 different services that a transport-layer protocol can offer: **
Data integrity 数据完整性
Throughput
Timing
Security
# Web and HTTP
3 components of web:
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL): serves as system for resources on web.
- Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP): specifies communication of browser and server.
- HTTP uses TCP as its underlying transport protocol
- A HTTP client first initiates TCP connection
- the browser and the server processes access TCP through their socket interfaces.
- Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML): defines structure, organisation and content of webpage.
# HTTP
Non-persistent HTTP 非持久性
**Persistent HTTP(1.1)**持久性
two types of HTTP messages: request, response
RTT(round-trip time 往返时间): time for a small packet to travel from client to server and back
Response status codes:
- 200 OK
- 301 Moved Permanently 永久移动
- 400 Bad Request
- 404 Not Found
- 505 HTTP Version Not Supported
# Cookies
Webserver transmits certain messages to a web browser so that the web server can monitor the user’s activity on a particular website, the messages are known as cookies.
Web server can monitor the user’s activity on a particular website
four components:
- 在响应头
- 在请求头
- 存储在用户主机被浏览器管理
- 后台数据库
Types of Cookies:
- Session Cookies 会话cookies
- Permanent Cookies 永久的
- Permanent Cookies 第三方
Use For:
- authorization
- shopping carts
- recommendations
- user session state (Web e-mail)
# Electronic mail
# Three major components:
user agents
mail servers (帮忙代收邮件)
SMTP (simple mail transfer protocol)
user to mail server
mail server to server
# SMTP
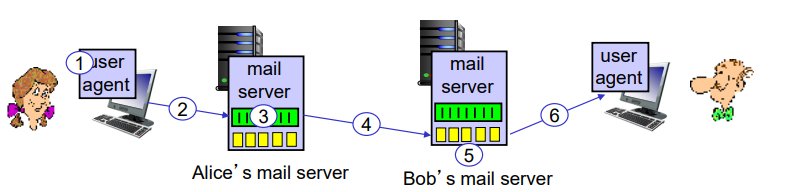
Post Office Protocol—Version 3 (POP3), Internet Mail Access Protocol (IMAP), and HTTP
# ⭐️DNS 域名系统
domain name system, application-layer protocol
why use?
- People prefer the hostname identifier more,更简单容易记住
- DNS is a directory service that provides a mapping between the name of a host on the network and its IP address
⭐️DNS services hostname to IP address translation:
❖ The IP address of www.someschool.edu. This is done as follows. ❖ 1. The same user machine runs the client side of the DNS application. ❖ 2. The browser extracts the hostname, www.someschool.edu, from the URL and passes the hostname to the client side of the DNS application. ❖ 3. The DNS client sends a query containing the hostname to a DNS server. ❖ 4. The DNS client eventually receives a reply, which includes the IP address for the hostname. ❖ 5. Once the browser receives the IP address from DNS, it can initiate a TCP connection to the HTTP server process located at port 80 at that IP address
Three different sections:
i. generic domains 通用(顶级)域名, ii. country domains 国家(顶级)域名, iii. and inverse domain(反解析,由IP映射到域名)
# P2P Applications
# BitTorrent(BT)
下载速度取决于参与者的数量,提供上行带宽Uplink bandwidth给下载者,已经下载的数据又提供给其他人共享下载
Download speed depends on the number of participants, providing Uplink bandwidth to downloaders and sharing the downloaded data with others
# CDN
Content Distribution Network 内容分发网络
A CDN is essentially a group of servers that are placed all over the globe with the purpose of accelerating the delivery of web content.
遍布全球的一组服务器,加速网络内容交付
Work:
▪ Manages servers that are geographically distributed over different locations. ▪ Stores the web content in its servers. ▪ Attempts to direct each user to a server that is part of the CDN so as to deliver content quickly.
# Socket programming
进程通信 process communication
Two socket types for two transport services: ▪ UDP: unreliable segment ▪ TCP: reliable, connection-oriented segments capturing a continuous byte-stream
# UDP:Connectionless
- no “connection” between client & server
- transmitted data may be lost or received out-of order
- UDP provides unreliable transfer of groups of bytes (“datagrams”) between client and server (不可靠传输)
# TCP:Connection-Oriented
client must contact server
三次握手(连接三次),可靠传输 TCP provides reliable, in-order byte-stream transfer (“pipe”) between client and server
详细见传输层
